Private Cloud Vs Public Cloud: Which Is Better For Your Data?: Complete Guide, Features and Details
In today’s digital landscape, data is the lifeblood of any organization. How you store, manage, and protect that data is paramount to your success. The cloud has emerged as a dominant force in data storage, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, the cloud isn’t a monolith. The two primary models, public and private cloud, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making the decision of which to choose a critical one. This isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer; the best choice depends heavily on your specific needs, budget, security requirements, and long-term goals.
Think of it like this: the public cloud is like renting an apartment in a large complex. It’s readily available, comes with amenities, and you only pay for what you use. The private cloud, on the other hand, is like building your own house. You have complete control over the design, security, and everything else, but it also requires a significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Both options provide shelter, but the optimal choice depends on your lifestyle and resources.
This guide will delve deep into the nuances of public and private clouds, exploring their features, advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations for choosing the right solution for your data. We’ll break down complex concepts into easily digestible information, empowering you to make an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding the differences between public and private clouds is crucial for optimizing your data management strategy and achieving long-term success.
Private Cloud Vs Public Cloud: An Overview
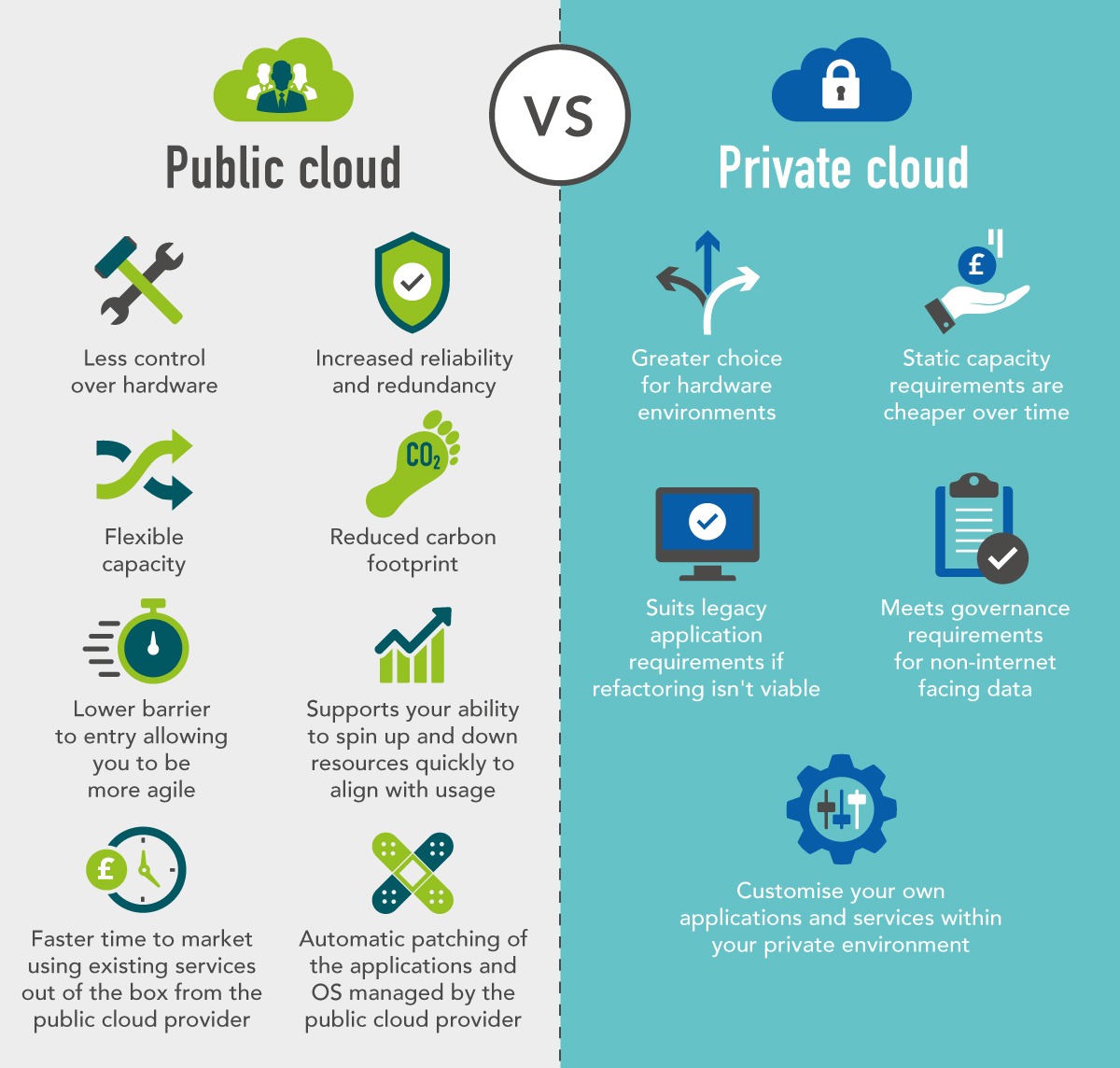
The core difference between public and private clouds lies in their infrastructure and accessibility. A public cloud is a multi-tenant environment where computing resources are owned and operated by a third-party provider (e.g., Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP)). These resources are shared among multiple users, offering scalability and cost-effectiveness. In contrast, a private cloud is a single-tenant environment dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises (within the organization’s own data center) or off-premises by a third-party provider.
Public Cloud: Shared Resources, Shared Responsibility
Public clouds offer a wide range of services, including compute power, storage, networking, and software. Users access these services over the internet and pay only for what they use, typically on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. The provider is responsible for managing the underlying infrastructure, including hardware, software updates, and security. This model is highly scalable, allowing organizations to quickly scale up or down their resources as needed.
Private Cloud: Dedicated Resources, Dedicated Control
Private clouds provide organizations with greater control over their infrastructure and data. They can customize the environment to meet specific security, compliance, and performance requirements. However, this control comes at a cost. Organizations are responsible for managing and maintaining the infrastructure, either in-house or through a managed service provider. This requires significant expertise and resources, making private clouds generally more expensive than public clouds.
Key Features and Characteristics
Understanding the specific features and characteristics of each cloud model is essential for making an informed decision.
Public Cloud Features
- Multi-tenancy: Resources are shared among multiple users.
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down as needed.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing model reduces capital expenditure.
- Accessibility: Access services over the internet from anywhere.
- Managed Infrastructure: Provider manages the underlying infrastructure.
- Wide Range of Services: Access to a broad range of compute, storage, and networking services.
- Global Reach: Providers offer data centers around the world, enabling global deployments.
Private Cloud Features
- Single-tenancy: Resources are dedicated to a single organization.
- Customization: Customize the environment to meet specific requirements.
- Control: Greater control over infrastructure and data security.
- Compliance: Easier to meet strict regulatory compliance requirements.
- Security: Enhanced security controls and isolation.
- On-premises or Off-premises: Can be hosted within the organization’s data center or by a third-party provider.
- Dedicated Resources: Resources are not shared with other users, ensuring consistent performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages: A Detailed Comparison
Let’s break down the pros and cons of each cloud model to help you weigh your options. For more information, you can refer to Cloud Computing as an additional resource.
Public Cloud Advantages
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure. Pay-as-you-go pricing reduces operational costs.
- Scalability and Elasticity: Easily scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating demand. This allows organizations to respond quickly to changing business needs.
- Reduced IT Burden: The provider manages the underlying infrastructure, freeing up IT staff to focus on other strategic initiatives.
- Faster Deployment: Deploy applications and services quickly and easily, accelerating time to market.
- Global Reach: Access to data centers around the world, enabling global deployments and improved performance for users in different regions.
- Automatic Updates: Providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that systems are always up-to-date.
Public Cloud Disadvantages
- Security Concerns: Sharing resources with other users can raise security concerns, although providers invest heavily in security measures.
- Compliance Challenges: Meeting strict regulatory compliance requirements can be challenging in a shared environment.
- Limited Customization: Limited ability to customize the environment to meet specific needs.
- Vendor Lock-in: Can become dependent on a specific provider, making it difficult to switch to another provider.
- Performance Variability: Performance can be affected by other users sharing the same resources.
Private Cloud Advantages
- Enhanced Security: Dedicated resources and enhanced security controls provide greater data protection.
- Improved Compliance: Easier to meet strict regulatory compliance requirements, such as HIPAA and PCI DSS.
- Greater Control: Greater control over infrastructure and data, allowing organizations to customize the environment to meet specific needs.
- Predictable Performance: Dedicated resources ensure consistent and predictable performance.
- Legacy Application Support: Can support legacy applications that may not be compatible with public cloud environments.
- Data Residency: Allows organizations to keep data within a specific geographic location to meet regulatory requirements.
Private Cloud Disadvantages
- Higher Costs: Requires significant upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure, as well as ongoing maintenance costs.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling resources can be more complex and time-consuming than in a public cloud environment.
- Increased IT Burden: Organizations are responsible for managing and maintaining the infrastructure, requiring significant expertise and resources.
- Slower Deployment: Deploying applications and services can be slower than in a public cloud environment.
- Underutilization: Resources may be underutilized, leading to wasted capacity and increased costs.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model: Key Considerations
Selecting the right cloud model requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs and priorities. Here are some key factors to consider:
Security Requirements
If your organization handles sensitive data or is subject to strict regulatory compliance requirements, a private cloud may be the better option. The enhanced security controls and isolation offered by a private cloud can help you protect your data and meet compliance obligations.
Budget
Public clouds are generally more cost-effective than private clouds, especially for organizations with fluctuating workloads. The pay-as-you-go pricing model allows you to pay only for the resources you use. However, if you require dedicated resources and enhanced security, a private cloud may be worth the investment.
Scalability Needs
If your organization requires high scalability and elasticity, a public cloud is the better choice. Public clouds allow you to quickly scale resources up or down to meet changing demand. Private clouds can be scaled, but it typically requires more planning and effort.
IT Expertise
If your organization has limited IT expertise, a public cloud may be the better option. The provider manages the underlying infrastructure, freeing up your IT staff to focus on other strategic initiatives. If you have the expertise to manage a private cloud, you can gain greater control over your infrastructure and data.
Compliance Requirements
Certain industries and regions have specific compliance requirements regarding data storage and processing. Understanding these requirements is crucial when choosing a cloud model. A private cloud often simplifies compliance, allowing for greater control over data residency and security measures.
Hybrid Cloud: The Best of Both Worlds?
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private cloud environments, allowing organizations to leverage the advantages of both models. For example, you might use a private cloud for sensitive data and critical applications, while using a public cloud for less sensitive data and less critical applications. This approach can provide greater flexibility, cost savings, and security.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Flexibility: Choose the right environment for each workload.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage the cost-effectiveness of public clouds for certain workloads.
- Scalability: Scale resources up or down as needed across both public and private clouds.
- Business Continuity: Ensure business continuity by replicating data and applications across multiple environments.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Data
The decision between public and private cloud depends on a variety of factors, including your organization’s security requirements, budget, scalability needs, and IT expertise. Public clouds offer cost-effectiveness and scalability, while private clouds provide enhanced security and control. A hybrid cloud approach can offer the best of both worlds. Carefully evaluate your needs and priorities before making a decision. Consider conducting a thorough assessment of your existing infrastructure, applications, and data to determine the optimal cloud strategy for your organization. Don’t be afraid to consult with cloud experts to get personalized guidance and support. Ultimately, the right choice is the one that best aligns with your business objectives and helps you achieve your long-term goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Private Cloud vs Public Cloud: Which Is Better for Your Data?
What are the key differences between a private cloud and a public cloud in terms of data security and control?
The primary difference lies in who manages and controls the infrastructure. A public cloud, like AWS or Azure, is owned and operated by a third-party provider. Your data is stored on their servers, and they are responsible for security. While they offer robust security measures, you have less direct control. A private cloud, on the other hand, is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party, but the organization has exclusive access and control over the infrastructure. This allows for customized security configurations and greater control over data governance, which is often preferred for highly sensitive data or strict regulatory compliance. However, this increased control comes with the responsibility of managing and maintaining the entire infrastructure, including security updates and patching.
How does the cost of storing data in a private cloud compare to the cost of storing data in a public cloud, considering both upfront investment and ongoing maintenance?
The cost comparison between private cloud and public cloud is complex and depends on several factors. A private cloud typically involves a significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and personnel to manage the infrastructure. Ongoing maintenance includes power, cooling, security, and IT staff salaries. While this provides predictable costs over time, the initial capital expenditure can be substantial. Public clouds, conversely, operate on a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating large upfront costs. You pay only for the storage and services you use. However, costs can escalate quickly as data volumes and usage increase. Factors like data transfer fees, storage tiers, and additional services need careful consideration. A total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis is crucial to determine the most cost-effective solution, considering both short-term and long-term needs.
When is a private cloud a better choice than a public cloud for data storage, especially considering factors like compliance requirements and data sovereignty regulations?
A private cloud is often the preferred choice when stringent compliance requirements and data sovereignty regulations are paramount. Industries like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), and government often face strict regulations regarding data location, access control, and security. A private cloud allows organizations to maintain complete control over their data and infrastructure, ensuring compliance with these regulations. Data sovereignty laws dictate that data must reside within a specific geographic region. With a private cloud, an organization can guarantee that their data remains within the required jurisdiction, mitigating legal and regulatory risks. While some public cloud providers offer region-specific data storage options, a private cloud provides a greater degree of control and assurance for meeting these complex compliance and sovereignty needs. The ability to customize security protocols and auditing mechanisms is another significant advantage in highly regulated environments.






