What Is Hybrid Cloud And Why Is It Crucial For Modern Businesses?: Complete Guide, Features and Details
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses face a constant barrage of challenges – from managing burgeoning data volumes to ensuring robust cybersecurity and maintaining cost-effectiveness. The traditional approach of relying solely on on-premises infrastructure often falls short in addressing these complexities. This is where the hybrid cloud model emerges as a powerful and versatile solution, offering a strategic blend of public and private cloud resources tailored to meet the unique needs of modern organizations.
The hybrid cloud isn’t just a technological trend; it’s a strategic imperative. It allows companies to leverage the scalability and cost-efficiency of public cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud, while simultaneously maintaining control and security over sensitive data and critical applications within a private cloud environment. This flexibility enables businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure, innovate faster, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the hybrid cloud, exploring its core components, key benefits, common use cases, and the crucial considerations for successful implementation. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or a business leader exploring cloud options, this article will provide you with a clear understanding of what hybrid cloud is and why it’s becoming increasingly crucial for modern businesses to thrive in the digital age.
What Is Hybrid Cloud?
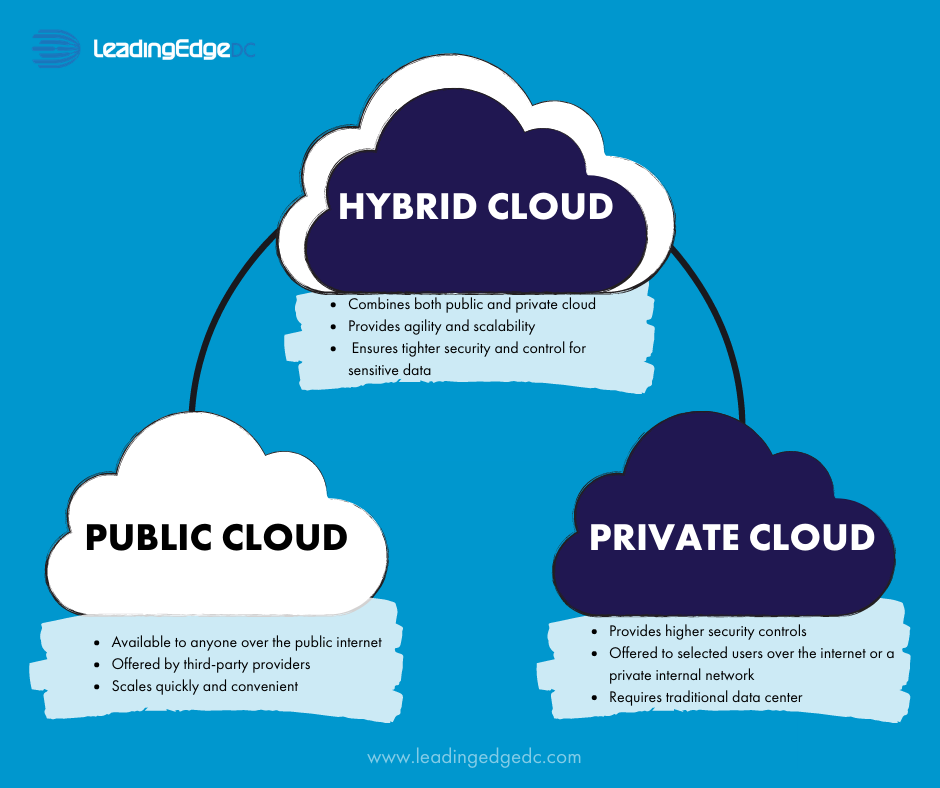
At its core, a hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines a public cloud and a private cloud. These two environments are connected, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This interconnection enables businesses to choose the optimal environment for each workload, balancing cost, performance, security, and compliance requirements. Think of it as having the best of both worlds: the agility and scalability of the public cloud combined with the control and security of the private cloud.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud
Understanding the components of a hybrid cloud is essential to grasping its overall functionality:
- Public Cloud: This is a multi-tenant environment where computing resources are owned and operated by a third-party provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). Businesses can access these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, making it ideal for workloads that require scalability and flexibility.
- Private Cloud: This is a single-tenant environment where computing resources are dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises (in the company’s own data center) or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control over security and compliance, making them suitable for sensitive data and critical applications.
- Networking: A robust and secure network connection is crucial for seamlessly connecting the public and private cloud environments. This connection enables data and applications to be transferred between the two environments, facilitating hybrid cloud functionality. Technologies like VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and direct connections are commonly used.
- Management and Orchestration: Tools and platforms are needed to manage and orchestrate workloads across both the public and private cloud environments. These tools provide visibility into resource utilization, automate tasks, and ensure consistent policies across the entire hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Why Is Hybrid Cloud Crucial for Modern Businesses?
The hybrid cloud model offers a compelling array of benefits that address the evolving needs of modern businesses. Here’s a detailed look at why it’s becoming increasingly crucial:
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of hybrid cloud is its ability to scale resources up or down on demand. Businesses can leverage the public cloud to handle peak workloads or seasonal spikes in traffic, while keeping steady-state workloads running in the private cloud. This flexibility ensures optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency.
Cost Optimization
Hybrid cloud enables businesses to optimize their IT spending by strategically allocating workloads to the most cost-effective environment. Non-critical workloads can be run in the public cloud, where pay-as-you-go pricing models can significantly reduce costs. Conversely, sensitive workloads can be kept in the private cloud, ensuring compliance and security without incurring the high costs of scaling on-premises infrastructure.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Hybrid cloud allows businesses to maintain control over sensitive data and comply with industry regulations. By keeping sensitive workloads in the private cloud, organizations can ensure that they meet stringent security and compliance requirements. At the same time, they can leverage the security features of the public cloud to protect less sensitive data and applications.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Hybrid cloud provides a robust foundation for business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR). Data and applications can be replicated between the public and private cloud environments, ensuring that they are available even in the event of a disaster. The public cloud can serve as a backup site, providing a cost-effective way to maintain business operations during an outage.
Innovation and Agility
Hybrid cloud enables businesses to innovate faster and respond more quickly to changing market conditions. Developers can leverage the public cloud to experiment with new technologies and deploy applications rapidly. The flexibility of the hybrid cloud allows organizations to adapt their IT infrastructure to meet evolving business needs.
Common Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud
The versatility of the hybrid cloud makes it suitable for a wide range of use cases across various industries. Here are some common examples:
Big Data Analytics
Businesses can use the public cloud to process and analyze large datasets, while keeping the data itself stored in the private cloud for security and compliance reasons. This approach allows organizations to leverage the powerful analytics tools available in the public cloud without compromising data security.
Application Development and Testing
Developers can use the public cloud to develop and test new applications, while deploying the production version in the private cloud. This allows them to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of the public cloud during the development process, while ensuring the security and stability of the production environment.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
As mentioned earlier, hybrid cloud is ideal for backup and disaster recovery. Data and applications can be replicated to the public cloud, providing a cost-effective and reliable backup site in case of a disaster. This ensures business continuity and minimizes downtime.
Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting is a technique where applications are typically run in the private cloud, but when demand spikes, the application “bursts” into the public cloud to handle the increased workload. This ensures that applications can handle peak demand without requiring businesses to over-provision their private cloud infrastructure.
Data Archiving
Businesses can use the public cloud to archive older data that is not frequently accessed. This allows them to reduce storage costs in the private cloud while still maintaining access to the archived data when needed. Public cloud storage is often significantly cheaper for long-term archiving than on-premises storage.
Considerations for Implementing Hybrid Cloud
Implementing a hybrid cloud requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
Security
Security is paramount in a hybrid cloud environment. Businesses need to implement robust security measures to protect data and applications across both the public and private cloud environments. This includes encryption, access control, and intrusion detection systems. It’s crucial to have a unified security policy that spans both environments.
Networking
A reliable and secure network connection is essential for connecting the public and private cloud environments. Businesses need to choose the right networking technology (e.g., VPN, direct connection) to ensure optimal performance and security. Network latency can significantly impact application performance in a hybrid cloud environment.
Management and Orchestration
Effective management and orchestration tools are needed to manage workloads across both the public and private cloud environments. These tools should provide visibility into resource utilization, automate tasks, and ensure consistent policies. Consider using a cloud management platform (CMP) to simplify the management of your hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Skills and Expertise
Implementing and managing a hybrid cloud requires specialized skills and expertise. Businesses may need to invest in training or hire experienced cloud professionals. Alternatively, they can partner with a managed service provider (MSP) to help them manage their hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Compliance
Businesses need to ensure that their hybrid cloud environment complies with all relevant industry regulations. This may require implementing specific security measures and data governance policies. Work closely with your legal and compliance teams to ensure that your hybrid cloud environment meets all applicable requirements.
Choosing the Right Hybrid Cloud Solution
Selecting the right hybrid cloud solution is crucial for achieving the desired business outcomes. Here are some factors to consider:
Workload Requirements
Identify the specific requirements of your workloads, including performance, security, and compliance. This will help you determine which workloads are best suited for the public cloud and which should remain in the private cloud.
Cloud Provider Selection
Choose a public cloud provider that meets your specific needs. Consider factors such as pricing, service offerings, security features, and geographic location. Evaluate multiple providers before making a decision.
Private Cloud Infrastructure
Determine whether you want to host your private cloud on-premises or with a third-party provider. Consider factors such as cost, control, and expertise.
Integration Capabilities
Ensure that the public and private cloud environments can be seamlessly integrated. This requires choosing compatible technologies and implementing robust integration tools.
Vendor Support
Select vendors that offer comprehensive support and documentation. This will help you troubleshoot issues and ensure the smooth operation of your hybrid cloud environment.
Conclusion
The hybrid cloud is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality that’s reshaping the IT landscape. Its ability to blend the agility of public clouds with the security of private clouds offers businesses a unique opportunity to optimize their IT infrastructure, reduce costs, and drive innovation. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this guide, businesses can successfully implement a hybrid cloud strategy that meets their specific needs and helps them thrive in the digital age. Embracing the hybrid cloud is not just about adopting new technology; it’s about adopting a new way of thinking about IT – one that’s flexible, adaptable, and aligned with the evolving needs of the business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about What Is Hybrid Cloud and Why Is It Crucial for Modern Businesses?
What exactly is a hybrid cloud computing model, and how does it differ from a purely public or private cloud solution?
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines a public cloud (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) with a private cloud (on-premises data center or private hosted infrastructure). It allows workloads and data to move between the two environments. Unlike a purely public cloud, which relies solely on third-party infrastructure, or a private cloud, which is entirely dedicated to a single organization, the hybrid cloud offers flexibility and choice. This enables businesses to optimize costs by running certain applications in the public cloud while keeping sensitive data or mission-critical applications within the secure confines of a private cloud. This combined approach allows businesses to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud while maintaining control and security over their most valuable assets. For more information, you can refer to Cloud Computing as an additional resource.
Why is adopting a hybrid cloud strategy becoming increasingly crucial for modern businesses, and what are the specific business benefits it offers?
Adopting a hybrid cloud strategy is increasingly vital for modern businesses due to its ability to provide unparalleled agility, scalability, and cost optimization. Businesses can leverage the public cloud for applications that require high scalability and elasticity, such as e-commerce platforms or data analytics, while maintaining sensitive data and critical applications in a secure, private environment. This flexibility allows companies to respond quickly to changing market demands and innovate faster. Furthermore, hybrid cloud helps businesses optimize costs by leveraging the pay-as-you-go model of the public cloud for variable workloads and reserving the private cloud for predictable, long-term needs. This strategic approach ensures efficient resource utilization and reduces overall IT expenditure. According to a recent Flexera report, 92% of enterprises have a multi-cloud strategy, highlighting the importance of hybrid cloud in modern business.
What are some of the key challenges and considerations when implementing a hybrid cloud infrastructure, and how can businesses effectively address them?
Implementing a hybrid cloud infrastructure presents several key challenges. Security is paramount; ensuring consistent security policies across both public and private environments requires careful planning and robust security tools. Data integration and management can be complex, as data needs to move seamlessly between the different environments. Businesses need to invest in appropriate integration tools and strategies to ensure data consistency and availability. Another consideration is managing the complexity of the hybrid cloud environment, which requires skilled IT professionals and robust management tools. Addressing these challenges involves implementing strong security protocols, adopting comprehensive data management strategies, and investing in skilled personnel and appropriate management tools. Furthermore, businesses should carefully evaluate the compatibility of their existing applications with the hybrid cloud environment and consider re-architecting them if necessary.






